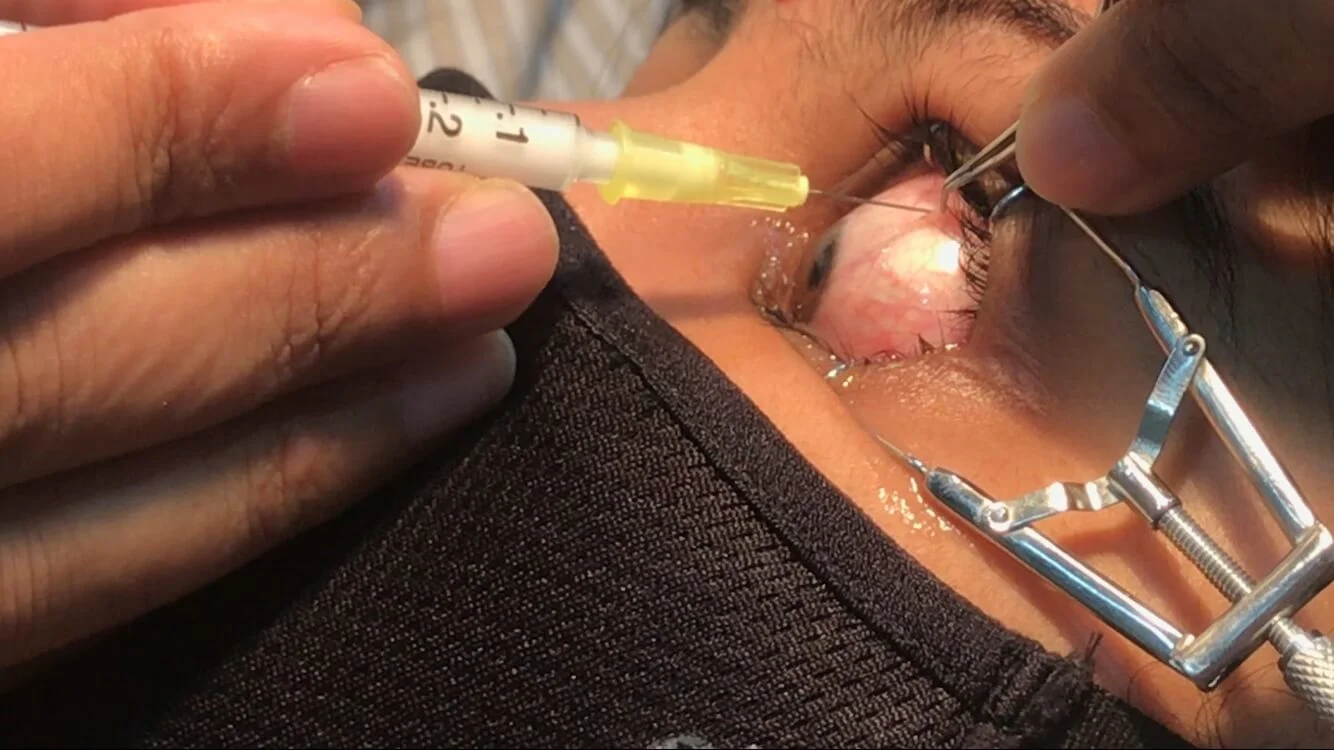
Eye injections may sound intimidating at first, yet they often serve as essential tools that protect vision and slow disease progression, helping patients maintain daily independence while addressing conditions that silently threaten long-term eye health.
What Makes Eye Injections an Important Treatment Option?
Eye injections matter because many retinal diseases respond best to targeted medication. These conditions often progress quietly at first. People may not realize their sight is changing until daily tasks feel harder. According to our editor’s research, many patients describe surprise after learning how quickly certain eye disorders evolve. Injections deliver medication directly to affected tissue. This precision allows faster response compared with oral treatments. Specialists rely on these methods when blood vessel changes affect the retina. Patients often feel relief knowing a structured plan exists. Treatment aims to preserve vision rather than restore lost clarity. People who start early usually maintain better long-term stability. The goal becomes protecting independence for years.
Why Do Doctors Recommend These Treatments?
Doctors recommend injections because retinal diseases typically require direct intervention. Conditions like macular swelling demand quick action. As a result of our editor’s reviews, early treatment prevents major complications. The retina cannot regenerate easily. Quick decline affects reading, driving, and facial recognition. Injections slow harmful changes. They block abnormal vessel growth. They reduce leakage that clouds vision. Patients often appreciate hearing that medication works locally. This reduces systemic side effects. Doctors evaluate each case carefully because timing matters. People with progressive symptoms receive tailored guidance. Recommendations focus on long-term preservation. This approach helps build confidence in the treatment plan.
How Do Eye Injections Work?
Eye injections deliver medication into the vitreous cavity. This allows direct contact with the retina. According to our editor’s research, this leads to faster absorption. Drugs used typically target inflammation or abnormal vessel growth. Anti-VEGF medications block proteins that cause leaking. Steroid injections reduce swelling. Antibiotic injections treat severe infections. Each type serves a different purpose. The key is precision. Medication reaches the exact tissue that requires support. This increases effectiveness. People often feel reassured once the process is explained. Understanding how the drug acts reduces anxiety. Clear explanations support smoother treatment sessions.
When Are Eye Injections Needed?
Eye injections become necessary when disease threatens central vision. Macular degeneration often requires repeated treatment. Diabetic eye disease also triggers swelling in the retina. As a result of our editor’s reviews, injections help reduce immediate risks. Retinal vein blockages cause fluid accumulation. Injections remove that pressure gradually. Severe infections inside the eye also require urgent medication. Without treatment, vision loss can progress rapidly. Specialists evaluate imaging results before decisions. Persistent swelling signals the need for intervention. Patients who delay treatment face higher risk. Early detection ensures better outcomes. Regular monitoring helps identify when injections are needed.
What Should Patients Expect During the Procedure?
The procedure usually lasts only minutes. Patients receive numbing drops first. This prevents discomfort. According to our editor’s research, most patients describe the process as easier than expected. Doctors clean the eye surface thoroughly. A small device keeps the eyelid open. The injection itself feels like slight pressure. There is no sharp pain for most individuals. Medication enters quickly. The patient rests briefly afterward. Vision may appear cloudy for a short time. Some people notice small floaters temporarily. These dissolve naturally. Clear instructions help patients feel confident. The experience becomes less intimidating after the first session.
Are There Risks Associated With Eye Injections?
Risks exist, though they remain rare. Infection risk is the most discussed. Proper cleaning reduces this possibility. As a result of our editor’s reviews, irritation is more common than serious complications. Mild redness may appear. Patients sometimes feel slight dryness. In rare cases, pressure inside the eye increases. Specialists check this during follow-up. Small floaters may appear but usually fade. People are advised to contact their doctor if severe pain develops. Early reporting ensures quick management. Understanding risks reduces fear. Patients feel more prepared when informed clearly. Awareness supports calm decision-making.
How Often Are Injections Needed?
Frequency varies based on condition. Some patients require monthly injections initially. Others need fewer sessions. According to our editor’s research, anti-VEGF treatments typically begin with a structured schedule. Doctors assess progress after several months. Many patients transition to longer intervals. Some conditions require ongoing maintenance. This depends on retinal response. People appreciate flexible scheduling once stability improves. Treatment goals shift gradually toward preservation. Regular imaging guides decisions. Consistent monitoring prevents setbacks. Frequency decreases for many patients over time. Personalized plans make the process manageable.
What Improvements Can Patients Expect?
Improvements vary depending on the condition. Many patients experience reduced swelling. Some regain partial clarity. As a result of our editor’s reviews, the main goal remains preventing further decline. Slowing disease progression helps maintain independence. People report better comfort during daily tasks. Reading may become easier. Faces appear clearer. Colors may look brighter. Stabilized vision reduces emotional stress. Improvements continue gradually over time. Consistency supports long-term results. Patients often feel hopeful when positive changes appear. Even small gains contribute to confidence.
How Should Patients Prepare Before an Injection?
Preparation remains simple. Patients should avoid rubbing their eyes. They should arrive with clean lashes. According to our editor’s research, some specialists recommend skipping makeup to reduce irritation. People should share recent medical changes. This helps doctors adjust plans. Relaxing beforehand helps reduce anxiety. Deep breathing can support calmness. Understanding the steps prevents surprise. Clear instructions improve comfort. Patients often feel more confident by the second visit. Preparation becomes routine quickly.
What Does Aftercare Involve?
Aftercare involves gentle routines. Patients should avoid touching the eye. Mild redness may appear for a day. As a result of our editor’s reviews, artificial tears reduce irritation. People should avoid heavy activity temporarily. Follow-up visits confirm stability. Doctors check for signs of pressure change. Patients may resume normal activities soon. Contacting a specialist for severe pain remains essential. Aftercare becomes familiar with experience. Simple habits ensure smoother healing. Many individuals feel reassured knowing side effects are temporary.
How Do Specialists Monitor Progress?
Specialists monitor progress through imaging. OCT scans reveal swelling levels. According to our editor’s research, these scans track subtle changes clearly. Doctors compare images over time. Improvement shows through reduced fluid. Stability indicates effective treatment. Follow-up exams guide next steps. Monitoring helps prevent sudden decline. Patients appreciate seeing visual proof of progress. Clear communication enhances trust. Regular checks maintain long-term safety. Monitoring remains central to treatment success.
Are Eye Injections Painful?
Most patients describe injections as mildly uncomfortable, not painful. Numbing drops work quickly. As a result of our editor’s reviews, pressure sensation is common. Sharp pain remains rare. Anxiety often heightens expectations. The actual procedure feels shorter than people imagine. Calm preparation reduces fear. Specialists reassure patients throughout. Mild irritation afterward resolves quickly. People often feel relieved once the first session ends. Comfort increases with familiarity.
